SCROLL
DOWN
A new public-private partnership, the Partnership for Food Traceability (PFT), has been launched to advance a shared vision for enhanced food traceability in alignment with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's (FDA's) Food Traceability Final Rule, fulfilling section 204(d) of the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA 204).
As an independent, sector-neutral forum for industry, regulators, industry associations, technical experts, and technology vendors, PFT aims to facilitate the wide coordination required to comply with the Food Traceability Final Rule. At present, PFT is the only independent forum that brings all parts of the supply chain together to make critical implementation decisions and define a shared vision for food traceability. The partnership includes participation from FDA, state, and local officials, enabling industry and regulators to share knowledge while working to advance traceability.
With a focus on defining business consensus and functional requirements for traceability, PFT is a forum for the exchange, gathering, and use of traceability data among supply chain partners. Additionally, PFT serves as an arena for technical implementation discussions among food industry stakeholders. The group will work toward defining a consistent set of business and functional requirements for traceability, a decision-making mechanism on industry's traceability implementation, and an organized plan for how the industry can successfully migrate to enhanced traceability.
PFT has begun its initial member sign-on period and will hold Board Member elections in October 2024. For more information and membership application, visit www.PFTraceability.org.

Public-Private Partnership for Traceability Aims to Advance Industry Toward FSMA 204 Compliance
USDA-FSIS Publishes Proposed Regulatory Framework for Salmonella in Raw Poultry
Image credit: Dr_Microbe/iStock / Getty Images Plus via Getty Images

On July 29, the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Food Safety and Inspection Service (USDA-FSIS) published an advance copy of its long-awaited regulatory framework for Salmonella in raw poultry products, setting an enforceable final product standard for the pathogen at certain levels—at which point it is determined to be an "adulterant"—and focusing on five serotypes of public health significance. The framework, which builds upon a draft framework released in October 2022, also requires Salmonella testing and monitoring in facilities.
The ultimate goal of the new regulatory framework is to reduce human cases of salmonellosis attributable to poultry products. FSIS intends to take science-backed actions that move the U.S. closer to the national Healthy People 2030 target of a 25 percent reduction in salmonellosis cases.
The revised regulatory framework for Salmonella in poultry "tentatively" determines Salmonella an adulterant in other raw chicken products at a certain level, and when a serotype of concern is present. More specifically, the proposed framework states that raw chicken carcasses, chicken parts, comminuted chicken, and comminuted turkey are adulterated if they contain any type of Salmonella at or above 10 CFU per milliliter (mL) or gram in analytical portion (i.e., mL of rinsate or gram of product) and contain any detectable level of at least one of the Salmonella serotypes of public health significance identified for that commodity.
Serotypes of Public Health Significance
The proposed Salmonella serotypes of public health significance identified for raw chicken carcasses, chicken parts, and comminuted chicken are S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium, and S. I 4,[5],12:i:-. For raw comminuted turkey, the identified serotypes are S. Hadar, S. Typhimurium, and S. Muenchen. These are the most highly virulent Salmonella serotypes associated with the respective products, based on the findings of FSIS chicken and turkey risk assessments.
However, the Salmonella serotypes of public health significance are likely to evolve over time as the serotypes most commonly linked to human illnesses change. If the final product standards are adopted, FSIS intends to reevaluate the serotypes of public health concern every 3–5 years, or whenever new information becomes available.
Sampling and Verification Program
If adopted, the final standards provide for a routine sampling and verification testing program for Salmonella in chicken parts, comminuted chicken, and comminuted turkey. FSIS would sample raw final products produced by an establishment and analyze them for Salmonella levels and serotypes to determine whether the final product is adulterated. If test results detect Salmonella at a level of 10 CFU/mL(g) or higher and at least one Salmonella serotype of public health significance, FSIS would consider products represented by the sampled lots to be adulterated and would issue a non-compliance record. All products in the lot represented by the sample would be prohibited from entering commerce.
Process Control, Monitoring, and Recordkeeping
Under the new framework, FSIS would establish new requirements pertaining to how facilities monitor and document whether their processes for preventing microbial contamination are in control. The proposed revisions are intended to clarify existing regulatory requirements related to process control monitoring in 9 CFR 381.65(g) and (h).
Establishments would be required to incorporate statistical process control monitoring principles into their microbial monitoring programs (MMPs). The proposed revisions would require that establishments use only validated, fit-for-purpose microbial sampling and analysis procedures; generate and record statistically meaningful microbial monitoring data; set benchmarks by which to evaluate microbial monitoring data; and otherwise define the statistical methods the establishment will use to evaluate the recorded data against the predefined limits.
FSIS has developed new guidance to help establishments meet the proposed updated requirements under 9 CFR 381.65(g). The new guidance includes an SPC sampling plan based on paired sampling for aerobic count at the rehang and post-chill locations, with a one-sided process control statistical model that charts and calculates against minimum monitoring criteria at the minimum required frequency. Establishments that incorporate the guidance into their MMPs would not be required to provide FSIS with additional scientific or technical information to support their chosen statistical methods. FSIS is proposing to make available to all poultry slaughter establishments an electronic spreadsheet file that is pre-programmed to calculate the monitoring measures for the guidance sampling plan, as results are entered. FSIS would also amend the recordkeeping requirements under 9 CFR 381.65(h) to require that establishments submit their microbial monitoring sampling results to FSIS electronically, via a web portal that is under development.
Not Required: Testing Incoming Flocks at Slaughter
In the October 2022 draft framework, FSIS considered requiring poultry slaughter establishments to characterize Salmonella as a "hazard reasonably likely to occur at receiving," mandating incoming flocks to be tested for Salmonella before entering an establishment. FSIS considered the available scientific research, as well as input from the National Advisory Committee on Microbiological Criteria for Foods (NACMCF), and concluded that the literature does not presently support the use of a threshold for test results at the receiving step to reduce or eliminate Salmonella from raw poultry products.
Comments on the proposed final regulatory framework have been extended to November 7, 2024 and may be submitted at www.regulations.gov, or by mail.
Due to the adverse health effects associated with exposure to dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate (DCPA), commonly known as Dacthal, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has issued an emergency order immediately suspending all registrations of the pesticide. The action represents the first time in 40 years that EPA has issued an emergency order to stop the use of a pesticide, and "follows years of efforts to require the submission of long-overdue data" to support a risk assessment, according to the agency.
Dacthal is a weed-killer that was previously approved for use in both agricultural and non-agricultural applications, mostly being used by industry for produce crops like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, and onions. Scientific literature has demonstrated that exposure to Dacthal during pregnancy affects fetal thyroid hormone levels, which can lead to low birth weight, impeded brain development, decreased IQ, and impaired fine motor skills.
At the time of the emergency order's issuance, Dacthal is undergoing registration review, a process for the regular reevaluation of registered agricultural chemicals to ensure they cause no unreasonable adverse effects on human health or the environment. A May 2023 assessment by EPA found health risks associated with DCPA use and application, even when personal protective equipment and engineering controls are used.

EPA Immediately Suspends Use of Herbicide Dacthal With Emergency Order
FDA Releases New Food Fraud Webpage
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has released a new website on economically motivated adulteration (EMA), including food fraud. The purpose of the website is to keep businesses and consumers informed on the latest food fraud developments.
The website includes links on how to report food fraud; examples of food adulteration; how food fraud is detected and monitored; enforcement and legal consequences, such as recalls, seizures, and import refusals; guidance documents to assist manufacturers and importers; and a list of import alerts.
EMA occurs when "someone intentionally leaves out, takes out, or substitutes a valuable ingredient or part of a food," according to FDA. EMA also occurs when a substance is added to a food to make it appear better or of greater value.
Food fraud is a common type of EMA that FDA investigates, but EMA also occurs with other products, including animal food and cosmetics. Some types of EMA are also misbranding violations. Estimating how frequently food fraud occurs or its exact economic impact can be challenging because food fraud is designed to avoid detection. Outside estimates by experts have found that food fraud affects 1 percent of the global food industry at a cost of approximately $10–$15 billion per year, although more recent expert estimates peg the cost as high as $40 billion per year.
Food fraud can also lead to major health issues and even death. Some examples include lead poisoning from adulterated spices and allergic reactions to a hidden or substituted ingredient that contains a small amount of just one food allergen.
Click here to visit FDA’s new EMA website.

Image credit: Dr_Microbe/iStock / Getty Images Plus via Getty Images
A recent study has demonstrated that the risk of foodborne Salmonella enterica infection from raw produce increases with high humidity, which is predicted to worsen due to climate change, and that certain plant diseases can aid the survival of Salmonella on leafy greens.
Fresh produce consumption is one of the most common routes of S. enterica infection, and the pathogen causes about 1.2 million illnesses in the U.S. every year. S. enterica can survive for extended periods of time on plants, and scientific literature has shown the ability of the pathogen to take advantage of changes to the microbial community on crops. For example, increased persistence of S. enterica has been observed on plants infected with bacterial phytopathogens, which are pathogens that cause disease in plants.
One such bacterial phytopathogen is Xanthomonas hortorum pv. Vitians, which causes a disease called bacterial leaf spot and is a common threat to leafy greens. Additionally, environmental factors like humidity are known to support Salmonella survival on healthy plants.
In the study, the researchers sought to understand how both humidity and bacterial leaf spot affect the ability of Salmonella to survive on leafy greens crops. To do so, they infected plants with X. Vitians and introduced Salmonella to the plants via water droplets to mimic contamination by irrigation or splash dispersal from the ground. The researchers varied the days along a plant's development at which X. Vitians was introduced, the periods of high and low humidity to which a plant was subjected, and how many days they waited after introducing Salmonella to a plant to measure its internal Salmonella population. The internal Salmonella population represents those pathogens that successfully move from a leaf surface to the interior of the plant, where microbes are protected from solar rays or postharvest sanitization treatments.
The researchers found that bacterial leaf spot caused by X. Vitians aids S. enterica survival and internalization within romaine lettuce, and that S. enterica's survival is dependent upon the timing of arrival during infection with bacterial leaf spot. If Salmonella is introduced to a plant too early or too late along its timeline of infection by X. Vitians, then either the plant's raised defenses or the plant disease itself will inhibit S. enterica survival, respectively.
Moreover, high humidity—predicted to increase globally as an effect of climate change—and the water-soaked lesions caused by bacterial leaf spot also enhance the ability of Salmonella to rapidly grow in lettuce.

Humidity, Bacterial Leaf Spot Increase Salmonella Survival on Leafy Greens
Following an evaluation of the risk of contracting a Vibrio infection from consuming seafood in the EU, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) warns that resistance to critical antibiotics is increasing in some Vibrio species, and that the prevalence of the pathogen in seafood is expected to increase globally due to climate change. Alongside a scientific opinion on the matter, EFSA also published a short animated video to explain the relationship between climate change and Vibrio in seafood.
EFSA's Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ Panel) reviewed the available scientific data on Vibrio occurrence and concentration in seafood, available analytical methods, pathogenicity to humans and virulence factors, and AMR and persistence mechanisms in different environments. BIOHAZ focused on the species most relevant to seafood: V. parahaemolyticus, V. vulnificus, and non-O1/non-O139 V. cholerae.
Overall, based on a synthesis of the available data, V. parahaemolyticus is present in approximately 20 percent of seafood, with one in five positive samples containing pathogenic strains. Bivalve mollusks and gastropods had the highest number of positive samples (27.8 percent and 28.8 percent, respectively). Pathogenic V. vulnificus was detected in about 6 percent of seafood samples, and was most prevalent in bivalve mollusks (9.9 percent). Non-choleragenic V. cholerae was detected in about 4 percent of the tested seafood samples.
Alarmingly, the BIOHAZ Panel's assessment found resistance to several antimicrobials, including those of last resort, among Vibrio isolates from seafood/clinical isolates from foodborne infections. The most common resistances were ampicillin (70–100 percent resistance based on seven studies) and streptomycin (30–70 percent, six studies) for V. parahaemolyticus; and colistin (87–100 percent, four studies), ampicillin (4–75 percent, five studies) and streptomycin (11–68 percent, four studies) for non-O1/non-O139 V. cholerae. AMR against medically important antimicrobials (i.e., carbapenems and highly important 3rd/4th generation cephalosporins) were increasingly found in the relevant Vibrio species and in imported seafood isolates.
EFSA recommends prioritizing the launch of an EU-wide baseline survey for relevant Vibrio species in pertinent seafood products at primary production and retail to be used as reference to study the effects of climate change on the prevalence of Vibrio in seafood.
In the meantime, to prevent foodborne Vibrio illnesses, EFSA stresses the importance of maintaining cold chain integrity during seafood processing, transportation, and storage. Additionally, to reduce the presence of Vibrio, the agency suggests measures like high-pressure processing, irradiation, and flash freezing of seafood products, followed by long-term frozen storage. Depuration, which involves placing live mollusks in tanks with clean, circulating seawater to filter out microbes, is also recommended for live oyster consumption.

Vibrio Becoming More Prevalent in Seafood Due to Climate Change; AMR Worsening
The European Commission has published a draft regulation that, if adopted, would require EU Member States to conduct whole genome sequencing (WGS) analysis during foodborne illness outbreak investigations, and to report the results of WGS analyses. Compliance with the regulation would be expected 18 months following its enactment.
The draft regulation would require Member States to conduct WGS on the isolates of certain important pathogens during the investigations of foodborne illness outbreaks, specifically: Salmonella enterica, Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli, Campylobacter jejuni, and Campylobacter coli. Member States would then be required to submit the results of WGS analysis to EFSA's and European Center for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC's) joint One Health system, through which EFSA can compare isolates from foods and human cases of illness to identify the vehicle of an outbreak.

Draft EU Act Would Require WGS Analysis for Foodborne Illness Investigations
In late August 2024, more than 200 food safety regulatory delegates gathered in Nairobi, Kenya to discuss the possibility of aligning national food safety standards across Africa. The two-day workshop on trade and food standards centered around a review of the ongoing joint work of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) to create a system of international African food standards.
Delegate Maryann Kindiki, Ph.D., National Codex Contact Point Manager at the Kenya Bureau of Standards (KEBS), suggested that African countries enter into mutual recognition agreements for one another's food safety standards, beginning with the alignment of standards within regional economic blocs, such as East Africa. Rectifying the differences between national food safety standards in Africa could help break down significant technical barriers to the intra-African trade of agricultural commodities.
According to the African Union, countries across the continent import an estimated $60 billion USD worth of food annually, despite being home to about 60 percent of the world's total arable land. Not only could a unified regime of food safety standards enhance the safety of the continent's food supply, but it could also catalyze African agricultural production, promote trade between African countries, and reduce the continent's dependence on international food imports.
Additionally, investments in certification infrastructure to facilitate food safety testing in support of harmonized standards could help enable the movement of agrifood products from surplus-producing countries to other areas of the continent experiencing a deficit of such goods, according to Peter Mutua, Manager for the KEBS Food Standards division.

African Experts Convene to Explore Alignment of National Food Safety Standards Across Continent

Mitzi Baum, M.Sc., CEO of Stop Foodborne Illness (STOP), will step down from her role by the end of 2024. STOP has expressed gratitude for Mitzi's leadership and collaborative spirit.
Editor's note: Check out this issue's Podcast Highlights section for an interview with Mitzi where she discusses her work with STOP!

BAUM
Mark Carter assumed the presidency of the International Association for Food Protection (IAFP) at the conclusion of the IAFP 2024 Annual Meeting in July. Carter also serves as Senior Software Product Manager for Hygiena.

CARTER
Universal Pure LLC appointed Frank Jimenez as Chief Executive Officer and a member of the Board of Directors.
The Global Cold Chain Alliance (GCCA) named Sara Goodman-Stickler as the organization's new President and CEO.

GOODMAN-STICKLER
Frostkrone Food Group appointed Stefan Körber as Managing Director for the company's German operations.
The Institute of Food Technologists (IFT) announced that Christopher Daubert, Ph.D. became IFT's 85th President on September 1.

DAUBERT
Columbia Grain International appointed industry veteran Stuart Beckman as Director of Safety.
Former Chipotle CEO Brian Niccol took over as CEO of Starbucks on September 9.

NICCOL
Ware Malcomb promoted Michael Cody to Practice Leader for its Industrial Cold and Food business sector across the Americas.
Kraft Heinz Co. named Todd Kaplan as its new Chief Marketing Officer of North America.

KAPLAN
Sprague Pest Solutions promoted Kolbin Bertilson, ACE to District Manager.
Tyson Foods Inc. appointed Devin Cole as the new President of the company's international business segment.

COLE
Sabert has appointed Richa Desai as Chief Sustainability and Strategy Officer.
Danièle Sohier has become President of AOAC International. Sohier also serves as Director of Scientific Affairs for Hygiena.

SOHIER
The Wendy’s Co. Board of Directors appointed Arthur B. Winkleblack as its non-executive Chair of the Board.
Arjoon Bose was appointed as Bel Group's Chief Marketing and Digital Officer.

Allergen Bureau Transitions to VITAL 4.0 Standard for PAL
Providing food manufacturers with a standardized methodology for determining whether precautionary allergen labeling (PAL) is appropriate for their products, the Allergen Bureau has introduced the latest version of its risk assessment tool, Voluntary Incidental Trace Allergen Labeling (VITAL®) 4.0. The VITAL Program, established in 2007, serves as a supplementary certification program for food manufacturers that are already certified to GFSI-recognized food safety schemes that include allergen management.
The VITAL PAL statement for cross-contact allergens, which reads as "May be present: allergen 'x,' allergen 'y,'" indicates a defined level of risk based upon scientific principles. By means of an interactive VITAL Action Level grid, action level concentrations are calculated using the reference dose and a reference amount specific to a food. The reference doses are the scientific basis of the VITAL Program, informing the appropriateness of PAL in foods that contain food allergen residues via cross-contamination.
The most crucial change in the updated VITAL 4.0 standard is the adoption of ED05–based reference doses, per JECRA recommendations. ED05 refers to the dose of the total allergen protein that is predicted to produce objective symptoms in 5 percent of the allergic population. The "Vital 4.0 Summary and FAQ Guide," among other VITAL resources, can be viewed here.

World's Largest Food Distributor Sysco Unveils its FSMA 204 Traceability Plan
Sysco Corporation has unveiled its comprehensive new plan to support compliance with FDA's Food Traceability Final Rule. Sysco will partner with iFoodDS to leverage its traceability, food safety and quality management solutions. The collaboration will give Sysco's extensive supplier network flexible, interoperable, and pragmatic options for data-sharing required by FSMA 204. Additionally, Sysco will work closely with its vast network of suppliers to implement traceability practices by providing education and guidance to align supplier processes with Sysco's traceability standards, a joint effort with iFoodDS. Finally, Sysco will establish an internal task force to monitor compliance and continuously improve traceability processes. This team will ensure that Sysco remains at the forefront of food safety and regulatory adherence.

UK Grocery Chain Morrisons is First Retailer to Raise Freezer Temperatures by 3 °C

Morrisons grocery chain has become the first UK retailer to raise its freezer temperatures to –15 °C, a commitment made in line with the Move to –15 °C Coalition, which is an industry effort to increase frozen food storage and transportation temperature standards for the sake of sustainability. The Move to –15°C Coalition advocates for the current industry standard for frozen food storage to be raised from –18 °C to –15 °C. According to the coalition, –18 °C is an archaic standard—set more than 100 years ago—and recent science shows that an increase of just 3 °C in freezer temperatures across the supply chain could greatly assuage the industry's environmental impact by cutting carbon emissions, saving energy, and lowering costs.
RESOURCES
The Think Tank on the Future of Food Safety Auditing was established in August 2023 in response to an urgent need for innovation in food safety auditing. The initiative aimed to elevate governance, processes, and practices. The Think Tank concluded its activities in April 2024, marking a significant milestone in the quest for a safer food supply chain.
Based on the vital insights and strategic recommendations from the Think Tank on the Future of Food Safety Auditing, outlined in the Think Tank's free whitepaper, the food and beverage industry must embrace and fast-track transformative change in food safety auditing practices. Industry leaders are called upon to elevate safety protocols beyond simple compliance. It is essential to view food safety audits as evolving tools for continuous enhancement, not just as checklists for compliance. Integrating digital technologies will boost audit efficiency, accuracy, and transparency.
There is also a pressing need to enhance the training and development of food safety auditors. This includes the technical aspects of auditing and soft skills crucial for effective communication and problem-solving. Promoting the auditing profession as a powerful career step is a clear need. The Future of Food Safety Think Tank whitepaper is publicly accessible and free to read and download.
'Future of Food Safety Auditing' Whitepaper Released

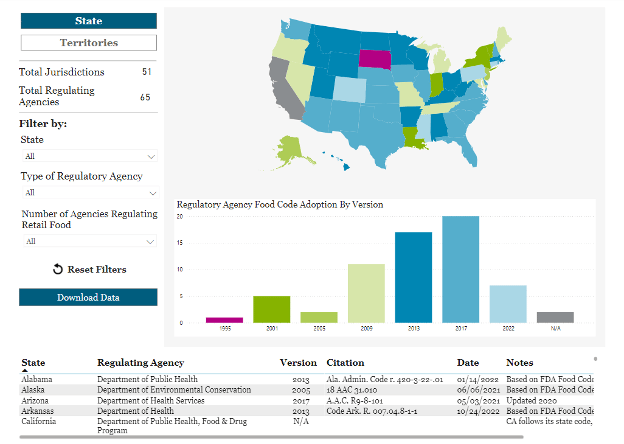
The Retail Food Safety Regulatory Association Collaborative, a coalition of representatives from seven organizations with a role in improving retail food safety in the U.S., recently updated its Food Code Adoption Map with improved data search functionality and visibility, as well as the new ability to download data. The Food Code Adoption Map is an interactive resource that shows the adoption of the FDA Food Code in each state and U.S. territory. According to the latest FDA Food Code Adoption Report, published in May 2024, only two states and two territories are at the "optimal level" of Food Code adoption, meaning they adopt the newest version in its entirety as soon as it is released.
Improved FDA Food Code Adoption Map Resource Available